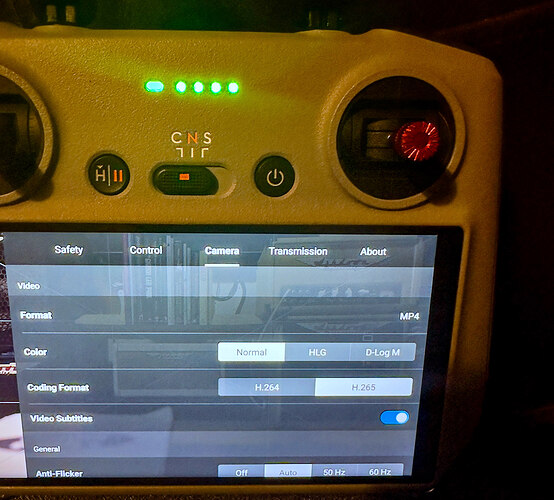
Video Encoding
H.264 and H.265 are two of the most widely used video compression standards for video encoding. They are used to reduce the size of a video file while maintaining its quality, making it easier to store, transmit and stream video content.
H.265, also known as HEVC (High Efficiency Video Coding), was introduced in 2013 as a successor to H.264. It provides better compression efficiency compared to H.264, meaning that it can encode video at a similar quality with a lower bitrate. This makes H.265 a better choice for applications where bandwidth or storage is limited. For example, H.265 is especially useful for encoding 4K and 8K ultra-high definition video, as it can reduce the file size of these videos by half compared to H.264.
In terms of quality, both H.264 and H.265 can provide high-quality video, but H.265 offers a noticeable improvement in terms of compression efficiency. This means that H.265 can maintain high-quality video even at lower bitrates, making it suitable for applications where bandwidth is limited.
One drawback of H.265 is that it requires more processing power compared to H.264 for encoding and decoding. This means that H.265 may not be suitable for devices with limited processing power, such as older smartphones and computers. Additionally, the licensing costs for H.265 can be higher compared to H.264.
In terms of compatibility, H.264 is more widely supported compared to H.265, as it has been in use for longer and is supported by a wider range of devices. However, H.265 is slowly becoming more widely supported as more devices adopt it.
D log is the flattest profile that DJI has, and it offers the highest level of dynamic range. while maintaining. the most flexibility when color grading in post. D Log M, on the other hand, is not as flat as D log, but it’s significantly easier to color grade than D log, making it the perfect choice for beginners.
Personally, I just use the defaults ie H.264 and Normal but drop the video sharpness factor down by -1.